A long wait on implementation of Labour Codes has come to an end with the notifications of implementation date of all Labour Codes effective 21-11-2025.
Except few provisions related to constitution of Central Advisory Board for fixation of minimum rates of wages and fixing national floor level wages and repealing of EPF(M&P) Act 1952 all other provision of all Labour Codes have been notified and implemented effective 21-11-25.
While the Indian Parliament has already passed the Code on Wages, 2019 in Aug 2019 and Code on Social Security, 2020, Occupation Safety, Health and working conditions Code, 2020 and Industrial Relations Code, 2020 in Sep 2020 with the aim to streamline and simplify the country’s existing and overlapping labour laws which received the President’s assent too, implementation of date has been elusive so far till 21-11-2025.
Brief on Labour Codes as a refresher:-
The Code on Wages, 2019:- Aims to regulate wage and bonus payments in all employments and aims at providing equal remuneration to employees performing work of a similar nature in every industry, trade, business, or manufacture.
The Code on Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions, 2020:- seeks to regulate the health and safety conditions of workers in establishments with 10 or more workers, and in all mines and docks.
The Code on Social Security, 2020:- consolidates nine laws related to social security and maternity benefits.
The Code on Industrial Relations, 2020:-Aims to improve the business environment in the country largely by reducing the labour compliance burden of industries.
Both Central and many State Govt have already issued draft Rules, and the final notification may be issued in few weeks from now.
There are 9 final Rules have already been notified by different states as given below: –

There are 9 draft Rules which are yet to be published by different State and UT as given below: –
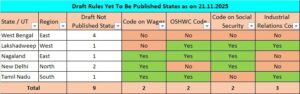
Since draft Rules issued by Central and State are yet to be notified for implementation date, few procedural aspects for implementing the provision of all four Codes cannot be implemented.
Impact of Labour Codes effective 21-11-2025
Code on Wages, 2019
- Revise or restructure the salary structure in line with the Wages definition
- Exclusion portion cannot be more than 50% total salary
- Existing structure shall be continued if inclusion portion is 50% or more and salary cannot be reduced now.
- Inclusion portion shall be equal to or more than the minimum wages.
- HRA cannot be part of the minimum wages
- Code is applicable to all employees irrespective of salary quantum. All registers to be maintained even under the existing Labour Laws to include all employees and not restricting to employees drawing upto Rs. 24000/- as gross salary.
- Bonus ceiling is yet to be notified by the Appropriate Govt. Till then employer shall follow existing Wage ceiling of Rs. 21000/-
- Procedural compliance need to be done only when Rules are notified.
Code on Social Security, 2020
- Provision of the PF Act and Schemes have not been notified hence current PF and Schemes need to be followed
- Current ESI Schemes shall be followed for one year till 20-11-2026
- Common Creche shall be followed if employer is not having a separate crèche while engaging 50 or more women employees irrespective of the applicability of ESI Act or ESI Chapter in this Code
- Telecommunication/ Insurance/ banking companies- Central government shall be the appropriate government
- Establishment having branches in more than one state – Central government shall be the appropriate government – Maternity benefit Act
- Fixed employees would be eligible for gratuity for their contract period if more than one-year post cessation of the contract. Since Rules are yet to be notified, procedural compliance need to be awaited and existing procedural compliance shall be followed.
Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020
- Appointment Order is to be issued to every employee by the employer. This include AO for contract labour by the contractor.
- Threshold limit of applicability of the Factory Chapter is 20 and 40 workers for the establishment using power or without power respectively having a manufacturing process
- Independent Director cannot be appointed as Occupier of the Factory. If any already appointed then this need to be revised immediately.
- Leave eligibility has been brought down to 180 days from 240 days in a calendar year
- Applicability of the Contract Labour Chapter is 50 or more contract workers for both Principal Employer and Contractor.
- Engagement of contract workers in the Core Activity is prohibited
- Welfare facilities to be provided by the Principal Employer only
- Canteen applicability is 100 or more workers
- Appointment of Safety Officer while engaging 500 or more workers
- Appointment of Welfare Officer while engaging 250 or more workers
- Applicability of Inter State Migrant workers chapter increased from 5 to 10
- Applicability of Inter State Migrant workers chapter would also be applicable for direct employees from other States having wages less than Rs. 18000/- per month
Industrial Relations Code, 2020
- Industry definition changed in line SC guideline on Triple test.
- App Govt is Central also for Telecommunications, Banking and Insurance Company and Metro Railways
- Supervisor drawing wages more than Rs. 18000/- are not workers
- Mass casual leave by 50% workers would be treated as Strike
- Grievance committee membership increased to 10 from 6
- Notice for strikes and lockout is to be given 60 days before and cannot go on strike within 14 days of giving such notice.
- Wilful go slow is considered as unfair labour practice
- Permission from App Govt is required for retrenchment or layoff if 300 or more workers are engaged
- Period of grievance application is reduced to one year from three years
- ID shall be raised within 2 years and reduced from 3 years
- Deposit to be done by the employer on retrenchment in Reskilling fund at 15 days of wages for every retrenched worker
- Applicability of Standing Order is increased to 300 workers
- Central Draft Rules for Standing Order shall be followed
- Trade Union having 51% workers as members would be the negotiating union. Negotiating council is to be formed having one member from each Trade Union having 20% workers as members
Conclusion
Since the Codes are notified, employer need to ensure to implement all direct provision of the Codes immediately effective 21-11-25. As Rules are required to be notified by Central and States, procedural compliance alone shall be done as per the existing provisions of the Labour Act.
Ensure seamless Labour Code readiness with Aparajitha’s expert end-to-end consulting and wage restructuring support. Talk to our Experts for Labour Code Readiness








5 Responses
Thank you for this clear and well-structured explanation of the Labour Codes. The practical approach makes complex provisions easier to understand for employers and HR professionals.
Outstanding.. your outlook on that is amazing
I need support in understanding new codes
Great article! The explanation of salary payment rules in India is very clear and helpful for employers. Timely salary compliance is crucial to avoid legal issues and maintain employee trust. Thanks for sharing such valuable insights.
nicely collated! State where rules already notified that comparison you can add and Rights and Duties of Employer and Employees can be elaborated